Power adapter efficiency is often mentioned in specifications, but many users underestimate how deeply it affects heat generation, product lifespan, and long-term energy costs. For industrial and commercial applications—especially high-power adapters—efficiency is not just about compliance, but about reliability and total cost of ownership.
This article explains what power adapter efficiency really means, how it influences heat and lifespan, the differences between Level VI and Level VII efficiency standards, and practical ways to reduce power loss.
What Does Power Adapter Efficiency Mean?
Power adapter efficiency is the ratio of output power delivered to the load versus the input power drawn from the mains.Efficiency=Input PowerOutput Power×100%
For example, if a 120W adapter draws 140W from the AC source, its efficiency is approximately 86%. The remaining 14% is lost as heat inside the adapter.
These losses mainly come from:
- Switching MOSFET conduction and switching losses
- Transformer core and copper losses
- Rectifier and output diode losses
- Control IC and auxiliary circuit consumption
How Efficiency Affects Power Adapter Heat and Lifespan
1. Heat Generation
Lower efficiency directly translates into higher internal heat. Even a few percentage points can make a significant difference at higher power levels.
- 120W adapter at 90% efficiency → ~13W heat dissipation
- 120W adapter at 85% efficiency → ~21W heat dissipation
That extra heat increases internal temperatures of MOSFETs, transformers, electrolytic capacitors, and PCB materials.
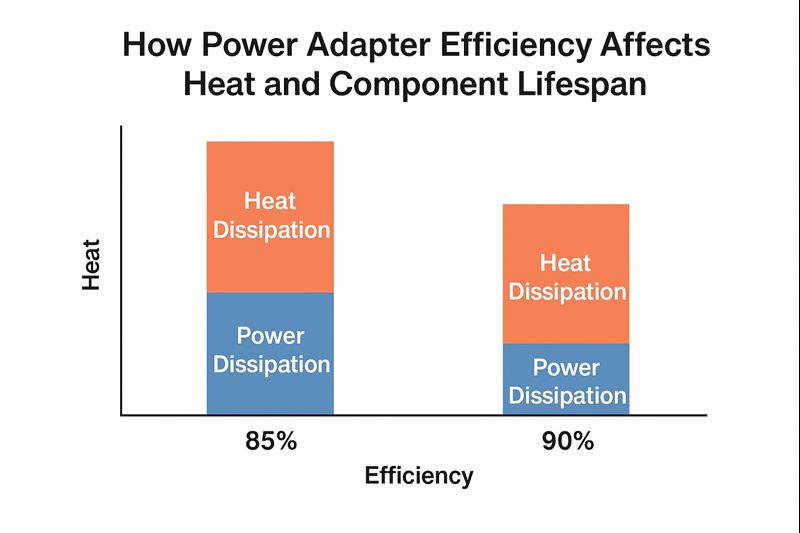
2. Component Lifespan
Heat is one of the primary factors limiting power adapter lifespan.
- Electrolytic capacitors typically halve their lifespan for every 10°C increase
- Semiconductor junction temperature directly impacts long-term reliability
- Excessive heat accelerates solder joint fatigue and insulation aging
Higher efficiency reduces thermal stress, extending service life—especially critical for industrial, medical, and 24/7 applications.
Power Adapter Efficiency Standards: Level VI and Beyond
Level VI Efficiency Standard (Current Requirement)
Level VI is currently the widely adopted and mandatory efficiency standard for external power supplies in many global markets, including the United States and Europe.
Key characteristics of Level VI include:
- Higher average efficiency measured at multiple load points
- Reduced no-load and standby power consumption
- Typical standby power requirement of ≤ 0.1W
Most modern compliant adapters are designed around Level VI requirements.
Looking Beyond Level VI: Future Efficiency Trends
While Level VI remains the current enforced standard, the power supply industry is actively discussing next-generation efficiency requirements, sometimes informally referred to as “Level VII”.
These future efficiency trends are expected to focus on:
- Further improvements in average efficiency
- Lower standby and no-load power consumption
- Better light-load efficiency performance
- Increased emphasis on real-world energy usage
At present, these concepts represent industry direction rather than finalized or mandatory regulations.markets, designing close to Level VII requirements offers a competitive advantage.
How to Reduce Power Loss in Power Adapters
Improving efficiency requires optimization at both circuit and layout levels:
1. Use Low-Loss Power Devices
- Select MOSFETs with lower Rds(on) and optimized switching characteristics
- Use synchronous rectification where applicable
2. Optimize Transformer Design
- Choose low-loss core materials
- Minimize leakage inductance
- Optimize winding structure to reduce copper loss
3. Improve PCB Layout and Thermal Design
- Short, wide high-current traces to reduce conduction loss
- Thermal vias under MOSFET pads to spread heat
- Proper spacing between hot components to avoid heat stacking
4. High-Efficiency Control Topologies
- LLC, QR flyback, or active clamp flyback topologies often outperform traditional designs
- Better light-load efficiency improves standby performance
What Is the Typical Standby Power Consumption of Adapters?
Standby (no-load) power consumption refers to the energy an adapter consumes when plugged in but not actively powering a load.
- Older designs: 0.3–0.5W
- Level VI compliant adapters: ≤ 0.1W
- Advanced high-efficiency designs: < 0.075W
Low standby power is especially important in applications where adapters remain plugged in continuously, such as consumer electronics, networking equipment, and medical devices.
Why Efficiency Matters Beyond Compliance
While efficiency standards are often viewed as regulatory requirements, their real value lies in:
- Lower operating temperatures
- Longer product lifespan
- Reduced field failure rates
- Lower energy bills over product lifetime
- Improved brand reliability and customer trust
For high-power adapters, efficiency is not a minor specification—it is a core performance parameter.
For high-power applications such as 120W adapters, medical power supplies, and PoE adapters, efficiency optimization becomes even more critical. At XJK Power, design efforts focus on reducing switching losses, improving thermal performance, and ensuring stable operation under continuous load conditions commonly required in industrial and European market applications.
Conclusion
Power adapter efficiency directly impacts heat generation, reliability, and energy consumption. Understanding efficiency standards such as Level VI and Level VII, along with practical loss-reduction techniques, helps designers and buyers make informed decisions.
At XJK Power, efficiency optimization is a core part of our power adapter design philosophy, ensuring stable performance and long-term reliability for industrial and commercial applications.