In many battery-powered applications—such as electric motors, portable equipment, and marine devices—manufacturers often restrict charging methods to proprietary AC adapters or dedicated solar controllers. When users attempt to power or recharge these systems from external batteries, selecting the correct DC power adapter becomes critical for safety, efficiency, and reliability.
This guide explains how to properly select a DC power adapter or DC-DC converter to replace proprietary charging solutions in lithium battery systems.
1. Understand the Original Power Adapter Specifications
The first and most important step is to analyze the original manufacturer’s power supply.
Typical specifications may include:
- Output Voltage: 29.4 V DC
- Output Current: 4.0 A
- Maximum Output Power: ~120 W
A 29.4 V output strongly indicates a 7-series (7S) lithium battery pack, as 29.4 V corresponds to the full-charge voltage (7 × 4.2 V).
Key takeaway:
The original AC adapter is already a regulated DC power supply, and any replacement solution must electrically behave the same way.
2. Why a Transformer Is Not the Correct Solution
In battery-powered systems, all energy sources and loads are DC.
- Transformers only work with AC voltage
- Battery-to-battery charging requires DC-DC conversion
Therefore, this is not a transformer selection problem, but a DC power regulation problem.
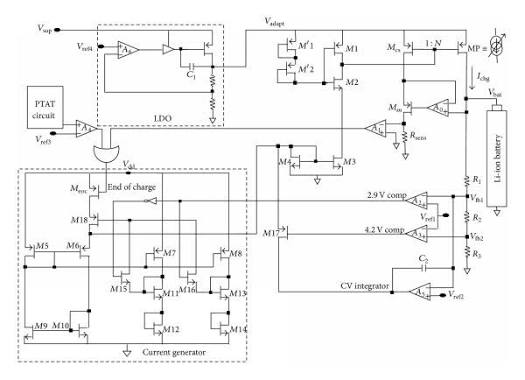
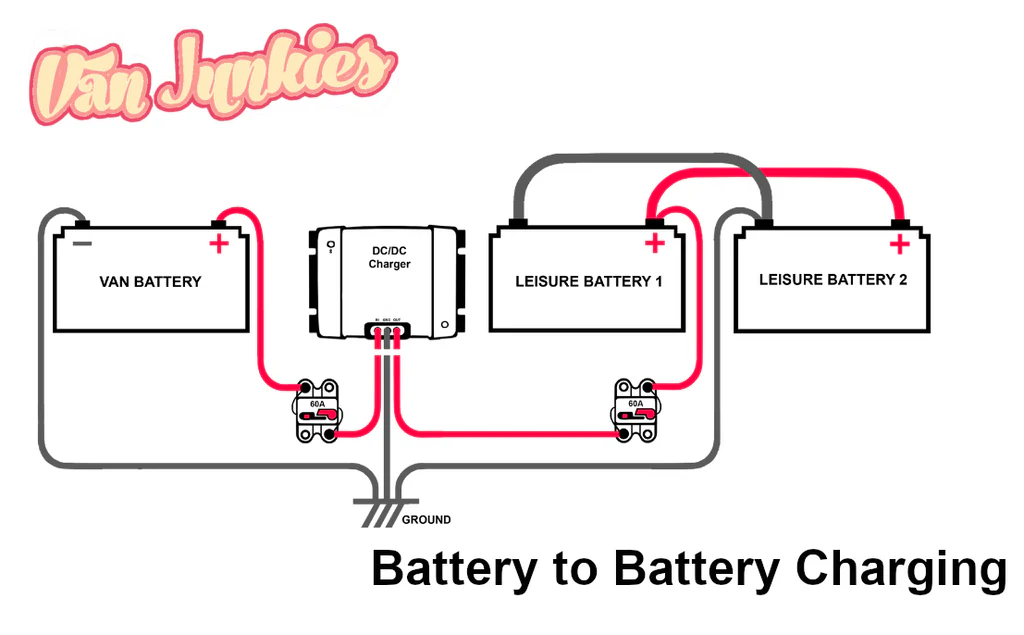
3. Common Mistake: Using Solar Charge Controllers
Solar charge controllers are frequently used as a workaround because they can:
- Accept a wide input voltage
- Regulate output for lithium batteries
However, in non-solar applications they introduce several disadvantages:
- Unnecessary voltage conversion stages
- Lower overall efficiency
- Additional cost and system complexity
- Charging logic optimized for solar panels, not batteries
For battery-powered input sources, solar controllers are functionally redundant.
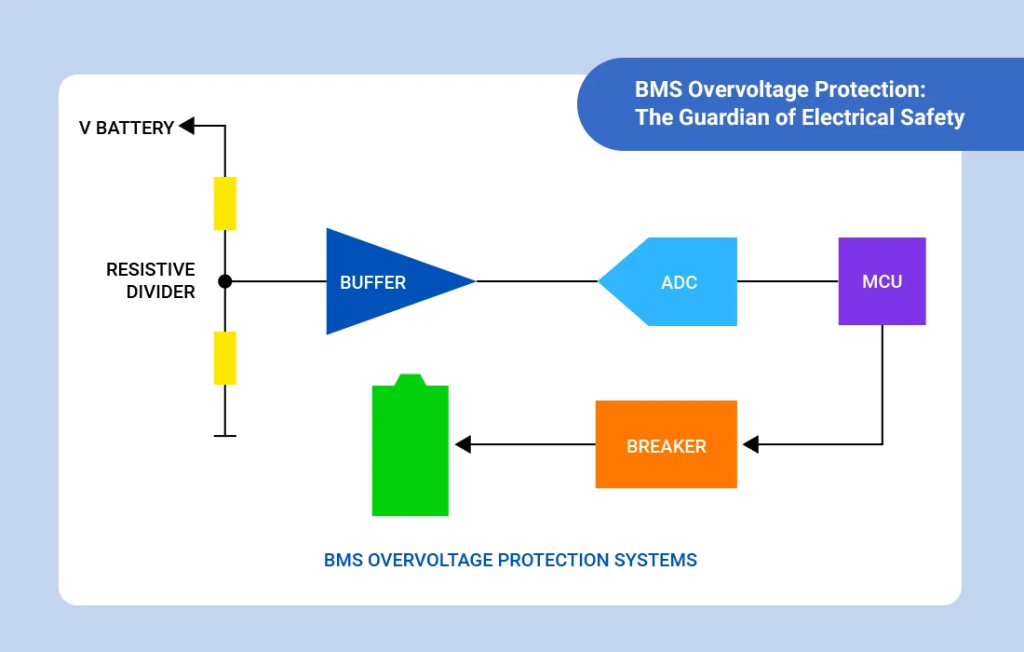
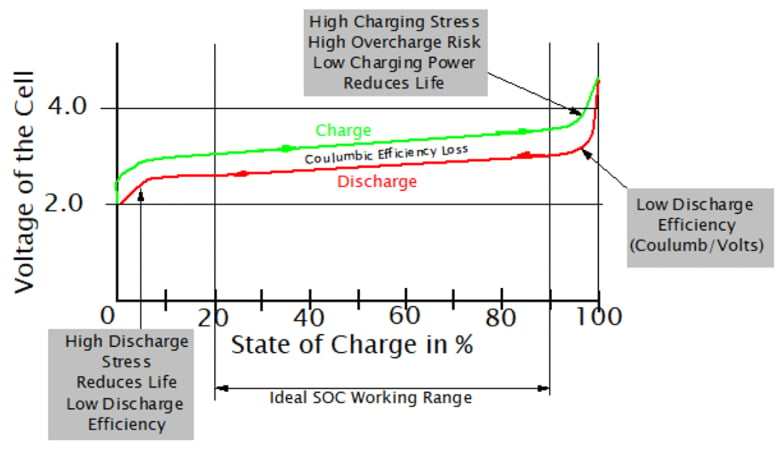
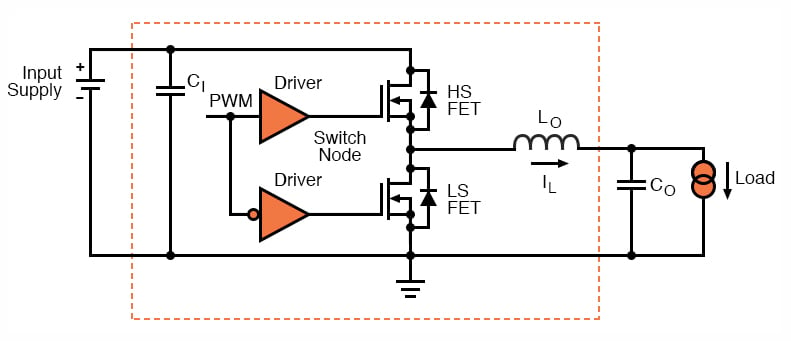
4. The Correct Power Solution: DC-DC Buck Power Adapter
For applications where the input source is a higher-voltage battery (for example, 36–42 V lithium packs), the optimal solution is a high-power DC-DC buck converter.
Recommended Electrical Characteristics
- Input Voltage Range: 30–60 V DC
- Output Voltage: 29.4 V DC (regulated, constant voltage)
- Output Current: ≥ 4 A
- Power Rating: ≥ 150 W (recommended for thermal margin)
- Efficiency: ≥ 90%
- Protections: OVP, OCP, SCP, OTP
This configuration directly replaces the original AC adapter without altering the charging behavior expected by the internal battery management system.
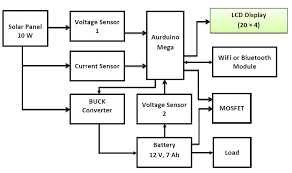
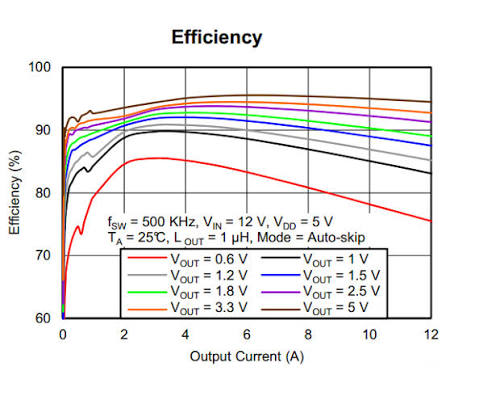
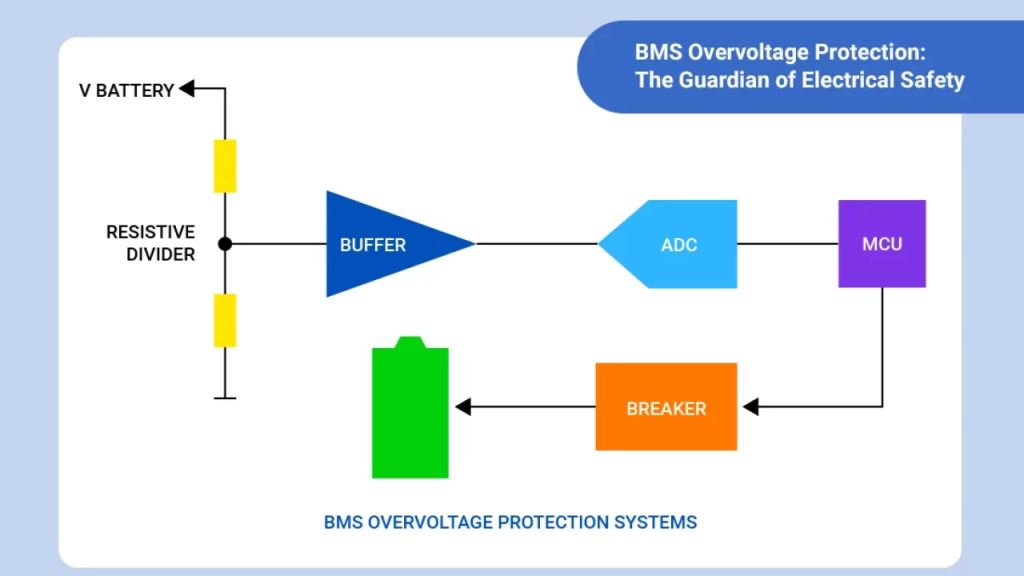
5. Safety and Reliability Considerations
When selecting a DC power adapter for lithium battery charging, always consider:
- Do not connect raw battery voltage directly to the load
- Ensure the output voltage is precisely regulated
- Select power ratings with sufficient thermal derating
- Use sealed or industrial-grade modules for outdoor or marine environments
Failure to meet these requirements may result in battery damage or system failure.
6. Conclusion
Replacing proprietary chargers or solar controllers with a properly selected DC power adapter or DC-DC converter is both practical and efficient when done correctly.
By matching the original adapter’s voltage, current, and power characteristics, a single high-quality DC power module can:
- Simplify system design
- Improve efficiency
- Increase reliability
- Extend usable operating time
This approach is widely used in e-mobility, industrial electronics, and portable power applications.




