Introduction: Efficiency Standards and the Overlooked Factor
Over the past decade, global regulations have pushed power supply manufacturers toward ever-higher efficiency levels. Standards such as DOE Level VI in the United States, CoC Tier 2 in the European Union, and Energy Star requirements have reshaped the way power adapters are designed, tested, and marketed.

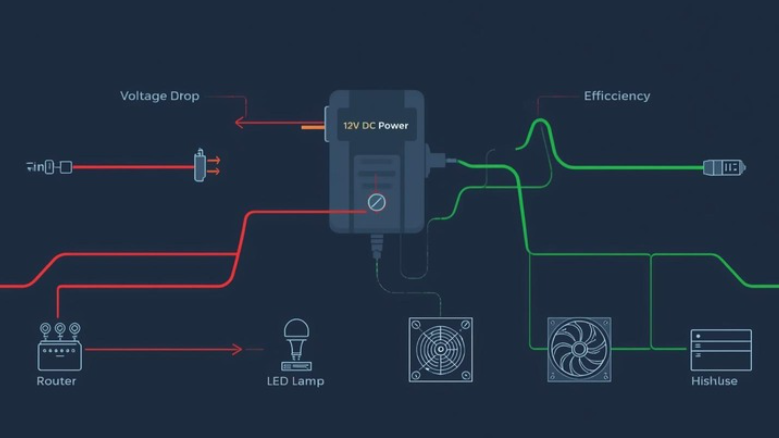
Most discussions in the industry focus on semiconductor advancements, circuit topologies, and thermal management. However, there is one component that often receives less attention despite its significant impact on real-world performance: the DC output cable.
The diameter of a DC cable directly affects voltage drop, current handling, and overall efficiency. As power standards become more demanding, cable specifications will play a crucial role in meeting both regulatory requirements and end-user expectations.
1. Cable Diameter and Efficiency: The Hidden Link
When a cable is too thin for the required current, its electrical resistance increases. This resistance leads to:
- Voltage Drop – lower voltage delivered to the device.
- Power Loss – wasted energy dissipated as heat.
- System Instability – devices may fail to operate properly under load.
For example, consider a 12V, 5A adapter with a 1-meter DC cable:
- Using AWG 24 results in a noticeable voltage drop (~0.4V).
- Using AWG 20 significantly reduces the loss (~0.1V).
In high-efficiency systems, even a 2–3% efficiency gap can determine whether a product passes or fails certification. More info refer to https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/.
| Cable Gauge (AWG) | Max Current (A) | Voltage Drop @ 12V / 1m | Efficiency Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 AWG | ~2A | ~0.4V (3.3%) | High loss |
| 22 AWG | ~3A | ~0.25V (2.1%) | Medium loss |
| 20 AWG | ~5A | ~0.1V (0.8%) | Low loss |
2. Regulatory and Market Trends
- North America (DOE Level VI): Requires tighter no-load power consumption and stricter active efficiency. While the standard doesn’t explicitly test cables, poor cable design can negate compliance.
- Europe (CoC Tier 2): Expands focus to cover efficiency under different load conditions, making end-to-end losses more critical.
- Medical and Industrial Applications: Compliance frameworks already consider long-term reliability and stable power delivery. Cable selection is increasingly part of quality audits.
Future Outlook: As efficiency standards evolve, regulators may start to include system-level efficiency testing, where the power adapter and cable are evaluated as a unit.
| Region | Standard | Focus | Relevance to Cable Loss |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | DOE Level VI | No-load power, active efficiency | Cable loss can cause compliance issues |
| EU | CoC Tier 2 | Efficiency under multiple loads | Cable selection affects system efficiency |
| Global | Energy Star | Consumer-focused efficiency labeling | Poor cables lower star rating |
3. Application Insights
- Consumer Electronics
Users often complain about “slow charging” or unstable devices. In many cases, the adapter meets specifications, but the cable diameter is too small to deliver full power. - Medical Devices
Hospitals require continuous, stable power. A poorly chosen cable not only reduces efficiency but may also compromise patient safety and compliance with medical standards (e.g., IEC 60601). - Industrial and IoT
As factories and smart systems adopt more low-voltage DC power distribution, cable losses over long distances become a critical cost and reliability factor.
4. Strategic Considerations for Manufacturers
Forward-looking power supply companies are beginning to:
- Integrate Cable Selection into Design Testing
Efficiency tests should include real cables, not just idealized conditions. - Offer Multiple Cable Options
Providing AWG 18, AWG 20, or AWG 22 versions allows customers to match performance with their specific application needs. - Enhance Supply Chain Standards
Consistency in copper quality and manufacturing ensures that every shipped unit meets both efficiency and safety expectations.
By treating the cable as part of the system—not an accessory—manufacturers can better align with regulatory requirements and customer performance demands.
| Manufacturer Type | Approach to Cable Selection | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Supplier | Treats cable as accessory | Risk of inefficiency & failures |
| Leading Supplier | Designs adapter + cable as a system | Higher compliance, customer trust |
Conclusion
Cable diameter is more than an engineering detail—it is an integral factor in achieving next-generation efficiency standards. As regulatory bodies continue to push for higher performance, ignoring cable losses could undermine years of innovation in power electronics.
Forward-looking companies will recognize that the “adapter + cable” combination defines real-world efficiency. By optimizing both, manufacturers can not only meet today’s requirements but also gain a competitive advantage in tomorrow’s power supply market.
For a practical guide on calculating cable size, see our article here.




